What is a Motion Reference Unit?
What is a Motion Reference Unit?
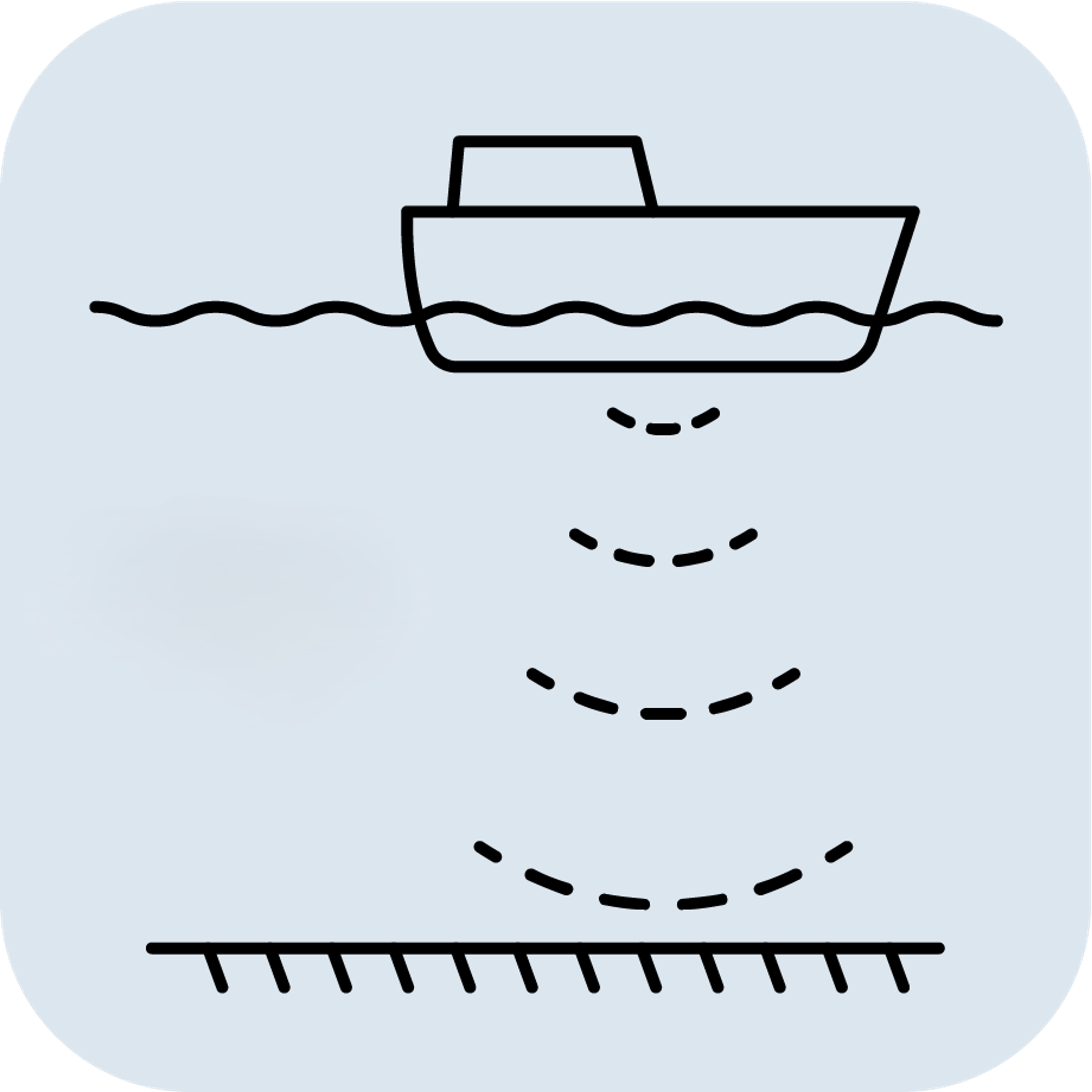
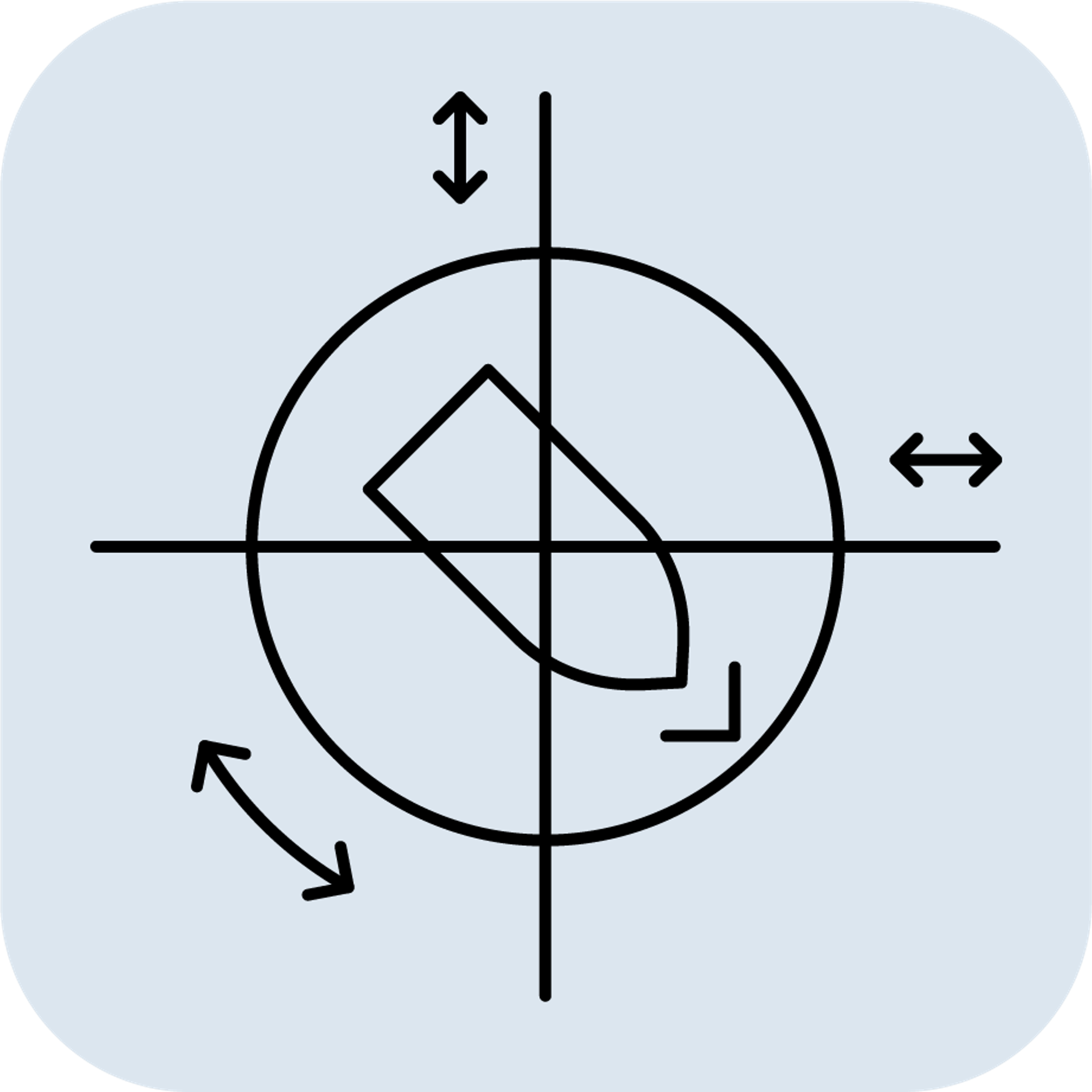
A motion Reference Unit (MRU) is a device that measures motion in all six degrees of freedom (DoF): roll, pitch, yaw & surge, sway and heave. The six DoF positions, velocities and accelerations are measured by the MRU using high-end gyroscopes and accelerometers (and sometimes magnetometers) and processed by advanced sensor fusion algorithms.
What is the limitation of an MRU?
An MRU has high accuracy Roll and Pitch measurements, and measures oscillatory Heave, Surge and Sway motions for wave periods at sea. Linear motions with very long periods, or steps, cannot be measured by an MRU as it assumes a 0 mean heave position.
What are the key features of an MRU?
- Sensors Included: High-end accelerometers and gyroscopes (and sometimes magnetometers).
- Output: Provides real-time, high-accuracy motion data in all six DoF (roll, pitch, yaw, heave, surge, and sway).
- Functionality: Optimized for dynamic environments, especially in marine settings, to provide accurate motion measurements under real sea conditions.
- Applications: Provides real-time, high-accuracy motion data in alle 6 DoF for monitoring, control, or instrument compensations within the maritime, offshore, and subsea sector.
Where is an MRU used?
- Monitoring systems: Ship motion monitoring, helideck monitoring, structural monitoring, and riser monitoring.
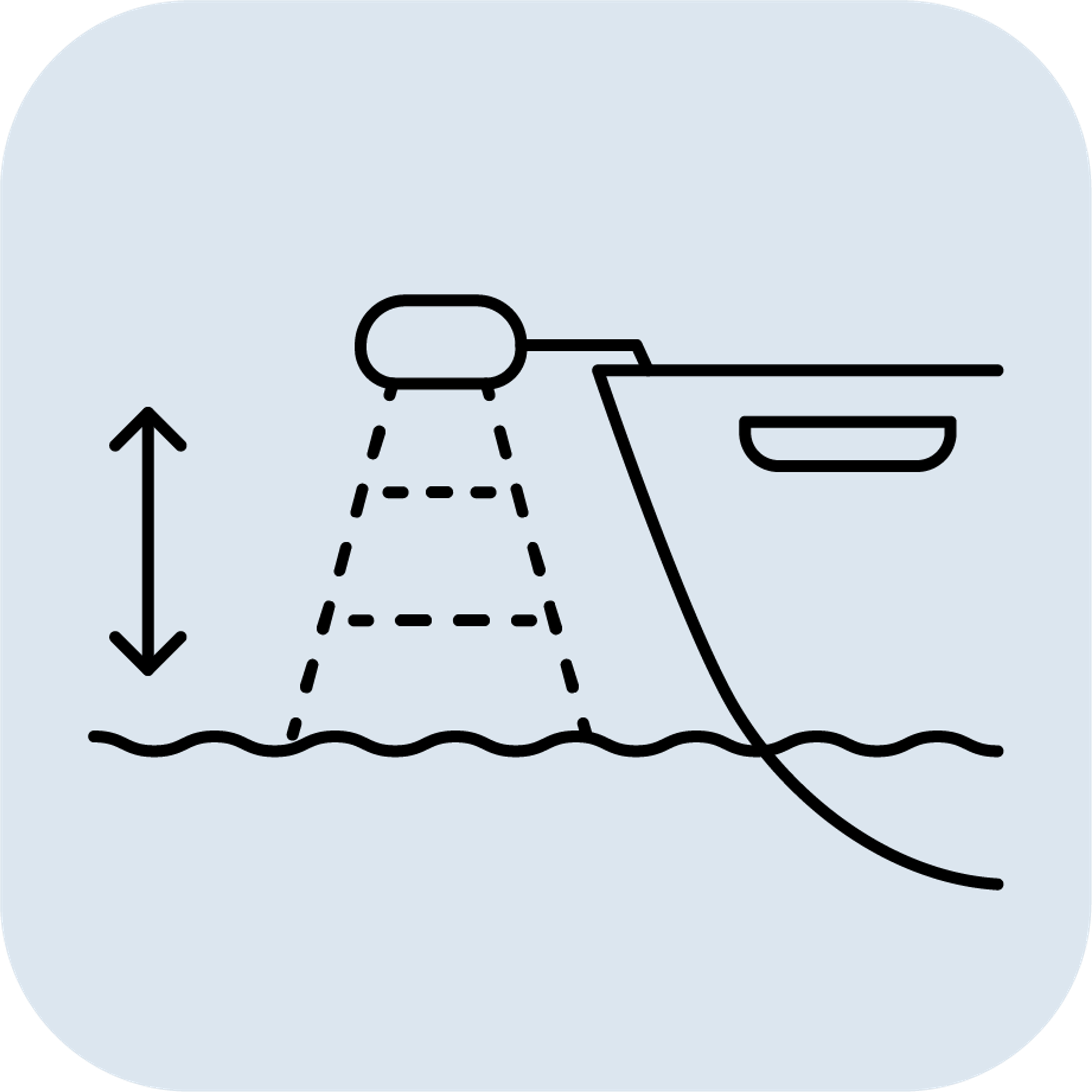
- Control systems: Active heave compensation in cranes, winches, and gangways.
- Instruments compensation: Hydrography, wave radar, dynamic position, and wind lidar.