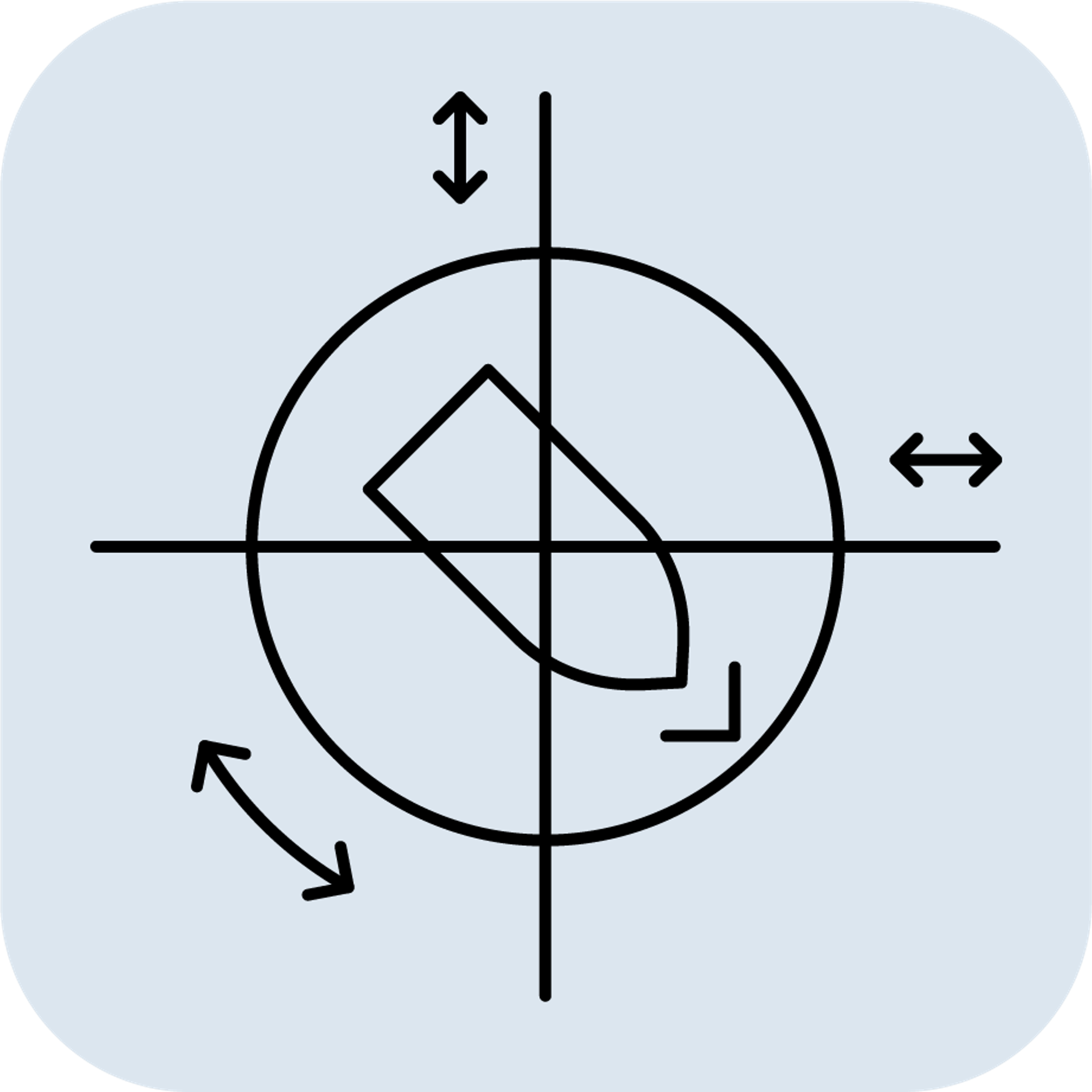
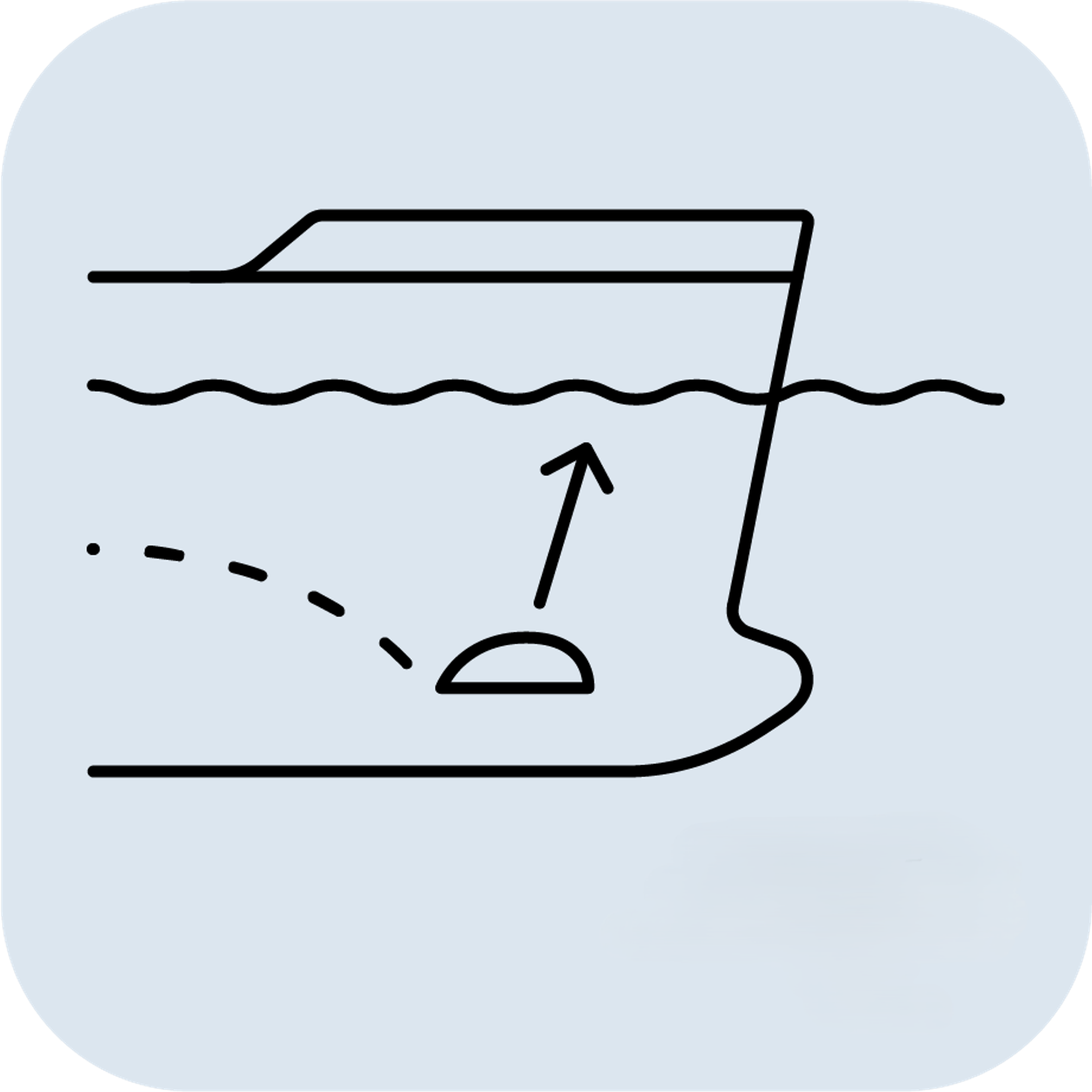
What is the difference between and Motion Reference Unit and a Vertical Reference Unit?
Motion Reference Unit (MRU)
Definition: A motion Reference Unit (MRU) is a specialized device and self-contained sensor that measures motion in all six degrees of freedom (DoF): Roll, Pitch, Yaw, Surge, Sway and Heave. The six DoF positions, velocities and accelerations are measured by the MRU using high-end gyroscopes and accelerometers (and sometimes magnetometers) together with advanced fusion algorithms. An MRU has high accuracy Roll and Pitch measurements, and measures oscillatory Heave, Surge and Sway motions for wave periods at sea. Linear motions with very long periods, or steps, cannot be measured by an MRU as it assumes a 0 mean heave position.
Vertical Reference Unit (VRU)
Definition: A VRU is an advanced device that measures the attitude (roll and pitch) of an object using high-end accelerometers and gyroscopes, combined with advanced sensor fusion algorithms. VRUs provide accurate roll and pitch measurements, even in dynamic environments.
Comparison of VRU with MRU: When you acquire a Norwegian Subsea VRU, this is essentially the same as the MRU. The only difference is that the VRU outputs roll and pitch only. It still has all the advantages of the MRU.
If you need lateral motions (heave, surge and sway), either position, velocity or accelerations, you will need to use the MRU.